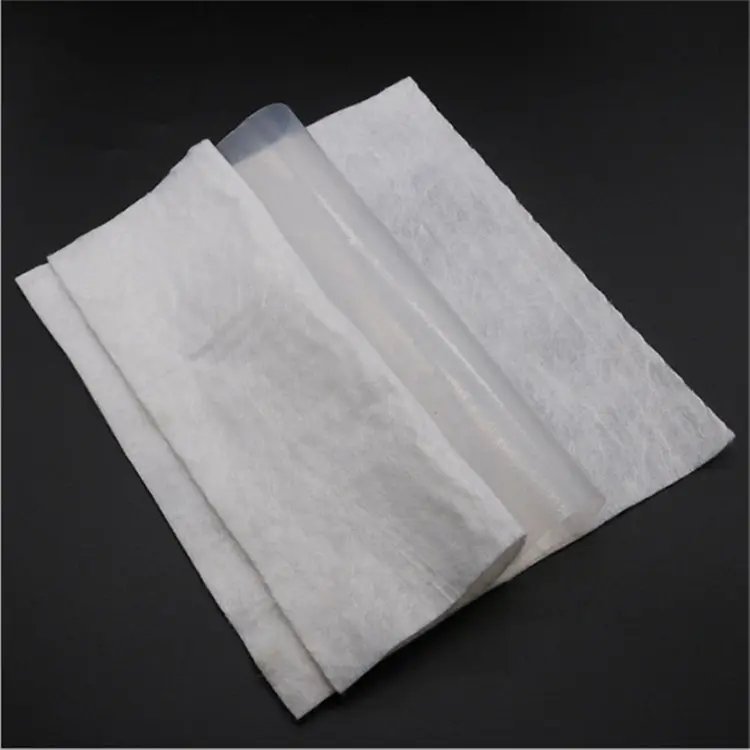
Ever wondered about the materials that make modern environmental projects a success? Let’s talk about composite geomembranes, a key player in this arena. These materials are not just another piece in the construction puzzle – they’re game-changers, making our engineering projects smarter and more sustainable. Let’s unravel their secrets together.
Composite geomembranes are advanced materials combining a geomembrane layer with geotextile fabric, offering both impermeability and mechanical strength. They are widely used in environmental protection, civil engineering, and water management.
Stay with us as we delve into the detailed aspects of composite geomembranes, from their robust durability and versatility to practical installation tips, ensuring you grasp their full potential in various applications.
Understanding Composite Geomembranes
Composite geomembranes are fascinating materials in the world of construction and environmental engineering. Let’s dive a bit deeper into what sets them apart:
The Composition
Composite geomembranes are an ingenious fusion of a geomembrane and a geotextile fabric. The geomembrane, typically made from robust materials like high-density polyethylene (HDPE), low-density polyethylene (LDPE), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), or ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM), acts as a resilient barrier against moisture, chemicals, and gases. This barrier is crucial in preventing seepage or contamination in sensitive areas. The geotextile component, which can be either woven or non-woven, complements the geomembrane by adding mechanical strength. It distributes stress and strain, preventing tearing or puncturing of the geomembrane, thereby enhancing the durability and lifespan of the system.
Composite Geomembrane Specifications
1. One geotextile and one geomembrane(geotextile: 100-1000g/m2; geomembrane thickness: 0.1-1.5mm)
2. Two geotextiles and one geomembrane(geotextile: 80-600g/m2; geomembrane thickness: 0.2-1.5mm)
3. One geotextile and two geomembranes (geotextile: 100-1000g/m2; geomembrane thickness: 0.1-0.8mm)
4. Many geotextiles and many geomembranes (geotextile: 100-1000g/m2; geomembrane thickness: 0.1-0.8mm)
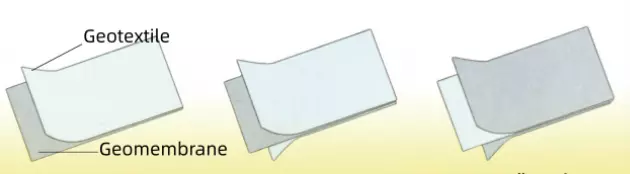
From left to right are:
One geotextile and one geomembrane
Two geotextiles and one geomembrane
One geotextile and Two geomembranes
The Functions
The beauty of composite geomembranes lies in their multifunctionality. While the geomembrane layer provides an impermeable barrier, essential for containment and waterproofing, the geotextile layer contributes tensile strength and protection. This dual functionality makes composite geomembranes a versatile choice for various applications. They are particularly effective in areas where both waterproofing and mechanical stability are critical. The geotextile layer not only protects the geomembrane during installation but also acts as a cushioning layer, protecting it from damage due to coarse aggregates or rough subgrades.
Enhanced Durability and Protection
The combined properties of these two materials result in a product that is far more durable and protective than either material could offer on its own. The geomembrane’s resistance to chemical and UV degradation, combined with the geotextile’s ability to resist punctures and tears, means that composite geomembranes are particularly suited for harsh environments and challenging projects.
Installation Efficiency
Composite geomembranes simplify the installation process. Instead of laying a separate protective layer and a geomembrane, the composite material allows for a single-step installation. This not only saves time but also reduces the likelihood of installation errors that can compromise the integrity of the system.
Installation Efficiency
Another advantage of composite geomembranes is their ability to be customized to specific project needs. Depending on the application, the thickness of the geomembrane and the type of geotextile (woven or non-woven) can be varied, allowing for a tailor-made solution that best fits the project’s requirements.
In summary, composite geomembranes stand out for their unique combination of impermeability, durability, and mechanical strength. These characteristics make them an ideal choice for projects that demand high-performance materials capable of withstanding a variety of environmental and mechanical challenges. Whether it’s for lining a hazardous waste landfill or reinforcing a water reservoir, composite geomembranes bring a level of assurance and reliability that’s hard to match.

Applications of Composite Geomembranes
Composite geomembranes, given their unique blend of features, play a pivotal role in a wide array of applications. Here’s an expanded look at where these versatile materials make their mark:
Environmental Protection
In the realm of environmental conservation, composite geomembranes are a key player. They are extensively used in landfill liners to prevent hazardous waste from contaminating the soil and groundwater. This feature is crucial in maintaining ecological balance and preventing pollution of the environment. Additionally, they are employed in capping closed landfills, effectively sealing off waste materials from the surrounding environment.
Environmental Protection
The role of composite geomembranes in water management cannot be overstated. They serve as reliable liners in ponds, canals, and reservoirs, efficiently preventing water loss due to seepage and ensuring optimal water conservation. In areas prone to water scarcity, this feature is invaluable. Moreover, they are used in the construction of artificial lakes and for the lining of irrigation channels, playing a significant role in agricultural water management and conservation efforts.
Civil Engineering
In civil engineering, composite geomembranes have revolutionized traditional practices. They are used to reinforce and stabilize the foundations in road construction, effectively preventing soil erosion and ensuring the longevity of the infrastructure. This application is particularly beneficial in areas with unstable or weak soil conditions. In addition, they are also used in the construction of tunnels and underground structures for waterproofing purposes, protecting these structures from water ingress and associated damages.

Agriculture
In the agricultural sector, composite geomembranes are used in a variety of applications. They are integral in the construction of irrigation systems, where they prevent water loss and help in efficient water distribution. Furthermore, they are used in aquaculture for pond lining, ensuring water retention and quality control, which is essential for healthy aquaculture practices.
Mining Industry
In mining operations, composite geomembranes are employed in heap leach pads, where they contain the leaching solution and prevent contamination of the surrounding environment. This application is vital in minimizing the environmental impact of mining activities.
Containment Solutions
These materials are also used in secondary containment solutions, such as for chemical storage areas or fuel stations, where they prevent potential spills or leaks from contaminating the ground.
Recreational Applications
Interestingly, composite geomembranes find their use in recreational applications as well, such as in the construction of artificial water bodies in golf courses and parks, enhancing the aesthetic appeal while ensuring environmental safety.
In essence, the applications of composite geomembranes are diverse and significant. Their ability to provide reliable containment and reinforcement solutions across various sectors – from environmental protection to civil engineering and agriculture – underscores their importance in modern construction and environmental management practices. These applications not only contribute to the sustainability and efficiency of projects but also play a crucial role in conserving natural resources and protecting the environment.
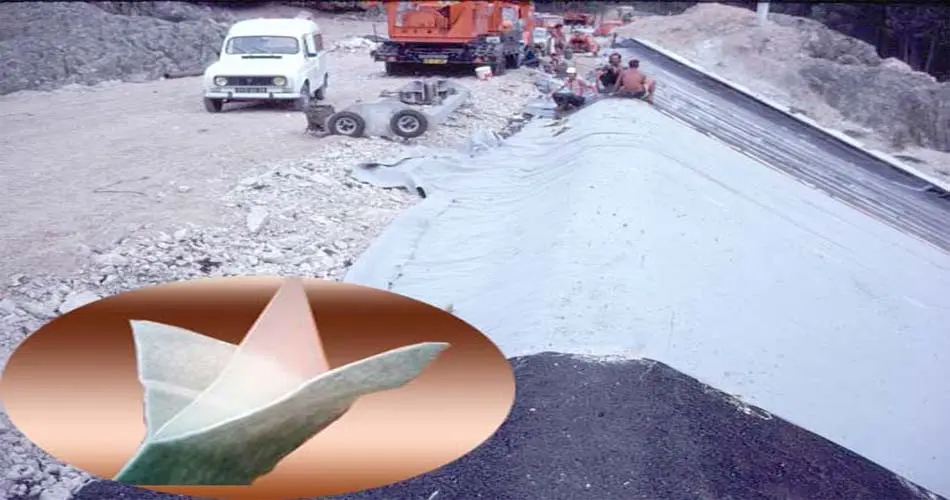

Why Choose Composite Geomembranes?
The decision to use composite geomembranes in a project is underpinned by several compelling reasons that make them stand out in the realm of geosynthetic materials. Let’s delve into the attributes that make them a preferred choice for many:
Durability
Composite geomembranes are renowned for their exceptional durability. Their resistance to punctures, tears, and chemical degradation makes them ideal for use in environments that are either chemically aggressive or mechanically challenging. This robustness ensures that they maintain their integrity over long periods, even under extreme conditions such as fluctuating temperatures, UV exposure, and biological factors. This prolonged lifespan reduces the need for frequent replacements, contributing to the longevity of the projects they are used in.
Versatility
The adaptability of composite geomembranes is another key advantage. They can be tailored to meet the specific requirements of various projects, whether it’s in terms of thickness, permeability, or tensile strength. This versatility makes them suitable for a wide range of applications, from environmental protection to water management and civil engineering projects. They can be effectively used in both large-scale industrial applications and smaller, more localized projects.
Cost-Effectiveness
In terms of economic value, composite geomembranes are a cost-effective solution. Their durability translates to less frequent need for repairs or replacements, leading to reduced long-term maintenance costs. Additionally, their ease of installation reduces labor costs and minimizes the time required to complete a project, further contributing to their cost-effectiveness.
Eco-Friendly
Composite geomembranes play a significant role in promoting sustainable construction practices. By preventing contamination and efficiently managing resources like water, they contribute to environmental conservation. Their use in landfills, for instance, helps prevent soil and water pollution, while in agricultural applications, they aid in water conservation and management. By minimizing environmental impact and aiding in the conservation of natural resources, composite geomembranes align well with the goals of sustainable development.
Enhanced Safety
Safety is a paramount concern in any construction or environmental project, and composite geomembranes contribute positively in this regard. By providing reliable containment and stabilization, they reduce the risk of environmental hazards and structural failures. This aspect is particularly important in applications like hazardous waste containment, where preventing leaks and breaches is crucial for safety.
Improved Project Efficiency
Using composite geomembranes often leads to an overall improvement in project efficiency. Their ease of installation, combined with their effective performance, means that projects can be completed more swiftly and with fewer complications. This efficiency is highly beneficial in time-sensitive projects or in scenarios where minimizing disruption is important.
In summary, the choice of composite geomembranes is justified by their durability, versatility, cost-effectiveness, eco-friendliness, safety enhancement, and contribution to improved project efficiency. These attributes make them an excellent choice for a wide range of applications, ensuring that projects are not only successful in the short term but sustainable and efficient in the long term as well.

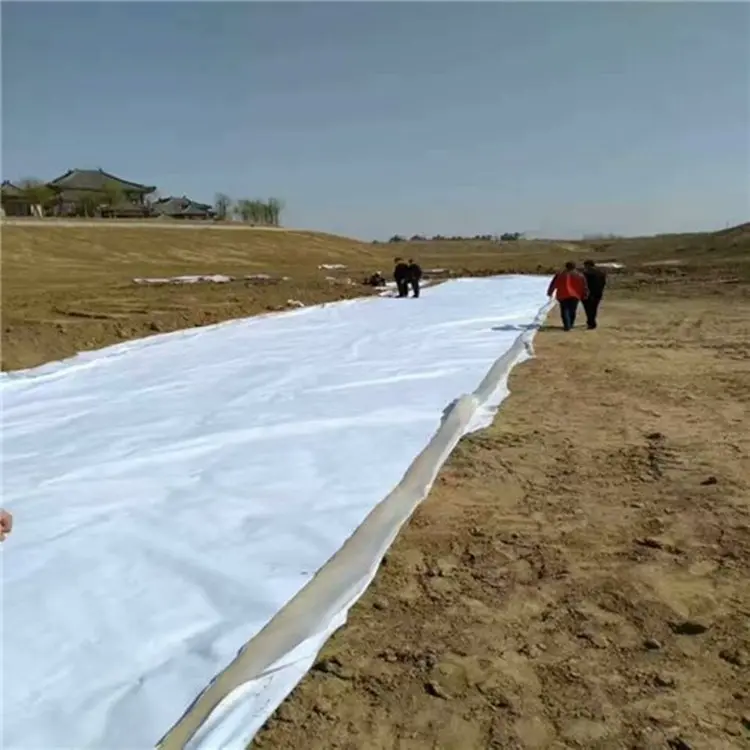
Installation Tips for Composite Geomembranes
Installing composite geomembranes effectively is crucial to maximize their performance and ensure the longevity of your project. Here are some expanded tips to guide you through the process:
Installation Method
When installing composite geomembranes, start by leveling the base with fine sand or clay. Lay the geomembrane gently to avoid overstretching, ensuring the ends are corrugated under the buried soil. Cover it with a 10cm fine sand or clay transition layer, followed by a 20-30cm protective layer of block stones or prefabricated concrete, carefully avoiding direct impact on the geomembrane. Secure the geomembrane to surrounding structures using expansion bolts and steel plate battens, and apply a 2mm thick layer of emulsified asphalt at the connections to prevent leakage.
Preparation of the Subgrade
The subgrade, or the surface on which the geomembrane will be laid, should be properly prepared. This involves grading, compacting, and smoothing the area to remove any objects or irregularities that might damage the geomembrane. Such as tree roots, stones, etc.
Correct Placement
Proper alignment of the geotextile and geomembrane layers is critical for the overall effectiveness of the composite geomembrane. This involves ensuring that there are no wrinkles or folds, which can create weak points and reduce the material’s effectiveness. The surface on which the geomembrane will be laid should be smooth and free from sharp objects that could puncture the material.
Proper Sealing
The impermeability of composite geomembranes largely depends on the quality of the seams. It’s essential to use the right sealing techniques, such as thermal or chemical welding, to ensure that the seams are watertight and secure. Pay special attention to areas around corners and edges, as these are often the most vulnerable to leaks. Regular testing of seam integrity, such as peel and shear tests, can help verify the quality of the seal.
Anchoring and Protection
Once laid, the geomembrane should be anchored securely to prevent displacement. In some cases, a protective layer, like a geotextile or a layer of soil, may be added on top of the geomembrane to protect it from mechanical damage, UV exposure, and other environmental factors.
Professional Help
For complex or large-scale projects, it’s advisable to engage with professionals who specialize in geomembrane installation. Their expertise can help avoid common installation mistakes and ensure that the geomembrane is installed to the highest standard. This is especially important in projects that require strict compliance with environmental regulations.
Quality Control
Throughout the installation process, maintain strict quality control practices. This includes inspecting the materials for defects before installation, monitoring the installation process closely, and conducting post-installation inspections to ensure that the geomembrane is performing as expected.
Training and Supervision
Ensure that the personnel involved in the installation are adequately trained and supervised. Proper handling and installation techniques are crucial to the success of the geomembrane application.
Consider Weather Conditions
Be mindful of weather conditions during installation. Extreme temperatures, precipitation, and wind can affect the handling and welding of geomembranes, potentially compromising the installation.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your composite geomembrane is installed effectively, providing optimal performance and durability for your project. Proper installation is key to harnessing the full benefits of this innovative material.

Conclusion
Composite geomembranes are more than just another construction material; they’re a crucial element in sustainable and efficient environmental and civil engineering projects. Understanding their composition, applications, and advantages helps professionals make informed choices, ensuring project success while contributing positively to the environment. Next time you come across a well-executed environmental project, chances are, composite geomembranes played a part in it!




