When selecting HDPE Geomembranes for your project, understanding the differences between those made from 100% virgin materials and recycled materials is crucial. Let’s explore these differences from various angles, including raw materials, lifespan, appearance, environmental impact, and application suitability.
100% Virgin HDPE Geomembranes, made from new HDPE resin, offer superior durability and consistency, ideal for high-stress applications. Recycled HDPE Geomembranes, using repurposed HDPE, provide a sustainable option with varied quality, suitable for less demanding uses.
Stay with us as we delve deeper into each material’s properties, helping you make the best choice for your specific needs.
Raw Material Source and Quality
Virgin HDPE Geomembranes: Sourcing and Consistency
Virgin HDPE Geomembranes are crafted from entirely new, unprocessed high-density polyethylene (HDPE) resin granules. This material is often procured from well-known and reliable manufacturers such as Sinopec, and international sources like Nordic Chemical. These companies are renowned for their stringent quality control measures, ensuring that the HDPE resin granules are of the highest standard. The use of these premium granules results in geomembranes with exceptional uniformity in their physical and chemical properties. This high level of consistency is crucial in applications where material reliability directly impacts the project’s success and safety.
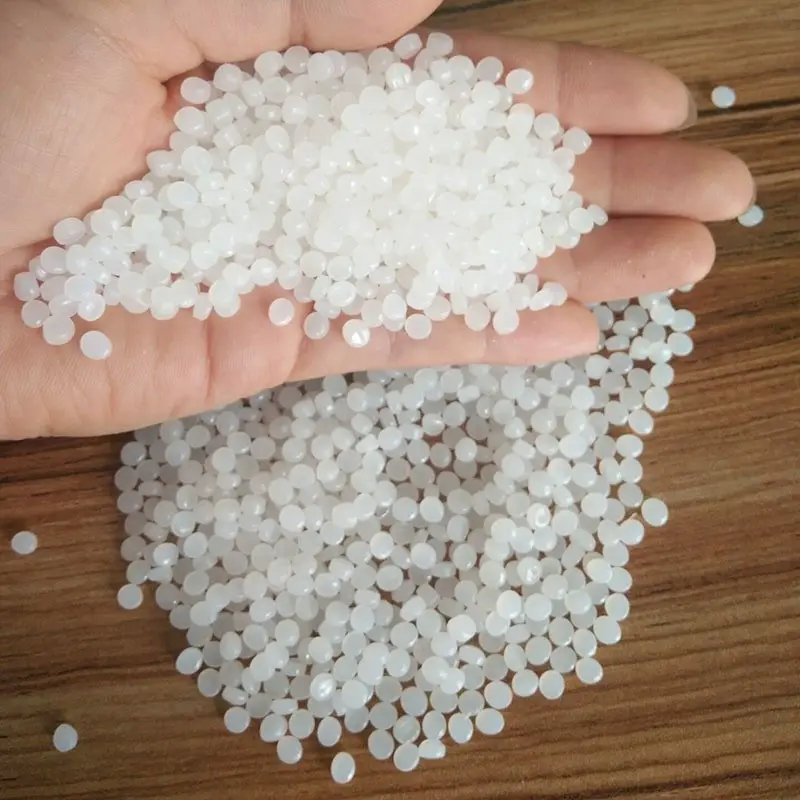

Recycled HDPE Geomembranes: Diversity and Variability
In contrast, Recycled HDPE Geomembranes are made from high-density polyethylene that has been reclaimed and reprocessed from various sources. This includes post-consumer products and industrial waste, which are collected, cleaned, and then processed to form HDPE resin granules. The diversity of the source materials means that recycled HDPE can vary in terms of quality and consistency. Factors such as the type of original HDPE products, the extent of degradation, and the effectiveness of the recycling process can greatly influence the final quality of the geomembrane. While advanced recycling technologies have significantly improved the consistency and reliability of recycled HDPE, it inherently possesses a degree of variability when compared to virgin material. This makes recycled HDPE geomembranes more suited for applications where top-tier material uniformity is less critical.
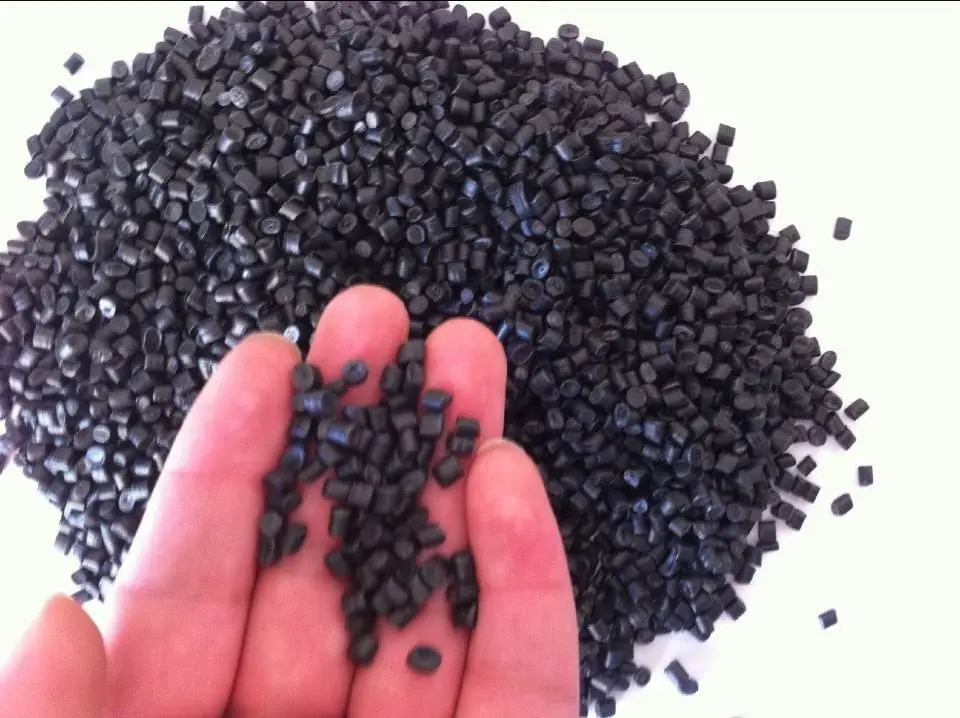

The choice between virgin and recycled HDPE geomembranes is thus influenced by the project requirements and priorities. While virgin material offers unparalleled consistency and reliability, recycled material is a more sustainable option that supports environmental conservation efforts
Lifespan and Durability
Virgin HDPE Geomembranes: Longevity and Resilience
Virgin HDPE Geomembranes are known for their remarkable durability and extended lifespan, which can range from 50 to 100 years when used in underground applications. This impressive longevity is attributed to the high-quality, new HDPE resin granules used in their production, which impart a strong resistance to various environmental stressors. These geomembranes are engineered to withstand harsh conditions, including exposure to chemicals, UV radiation, and extreme temperatures. Additionally, their resistance to mechanical stress, such as tearing and puncturing, is significantly higher compared to their recycled counterparts. This makes virgin HDPE Geomembranes particularly suitable for critical applications where long-term reliability is essential, such as in hazardous waste containment, landfill liners, and large-scale water conservation projects. The extended lifespan not only ensures the safety and integrity of the projects they are used in but also provides long-term cost-effectiveness despite the higher initial investment.
Recycled HDPE Geomembranes: Variability and Practical Life Expectancy
Recycled HDPE Geomembranes, while offering a more sustainable and cost-effective solution, generally have a shorter lifespan compared to virgin material geomembranes. Typically, they can last up to 10 years, particularly in above-ground applications. The reduced durability can be attributed to the inherent variability in the quality of the recycled HDPE resin. This variability arises from factors such as the diversity of the recycled sources, the degree of polymer degradation in the recycled material, and the efficacy of the recycling process itself. These factors can lead to inconsistencies in the physical properties of the geomembranes, such as reduced tensile strength and diminished resistance to environmental factors like UV exposure and temperature extremes. Consequently, recycled HDPE Geomembranes are more suited to less demanding applications, where the longevity and robustness of the material are not the primary concerns. Examples of such applications include temporary lining solutions, agricultural ponds, and secondary containment areas where frequent replacement is feasible and cost-effective.
The decision between virgin and recycled HDPE Geomembranes in terms of lifespan and durability depends largely on the specific requirements and priorities of the project. While virgin HDPE offers unmatched longevity and strength, recycled HDPE is a viable option for projects where environmental sustainability and cost are significant considerations.
Appearance and Flexibility
Virgin HDPE Geomembranes: Aesthetic Quality and Adaptability
Virgin HDPE Geomembranes stand out for their exceptional aesthetic qualities. They typically showcase a smooth, glossy finish, reflecting their premium, untouched material composition. This sheen not only serves as a visual indicator of quality but also implies a certain level of manufacturing finesse. The pristine nature of the virgin HDPE resin granules contributes to this refined appearance, free from imperfections commonly seen in recycled materials.
In terms of flexibility, virgin HDPE Geomembranes are highly adaptable, capable of conforming to various shapes and contours. This flexibility is a crucial attribute, especially in applications requiring the geomembrane to fit snugly around irregular surfaces or in uneven terrain. It also contributes to the ease of installation and the ability to withstand differential settlement without compromising integrity. The high flexibility ensures that these geomembranes maintain their structural integrity under mechanical stresses, such as stretching or bending, which is vital in preventing leaks and breaches over time.
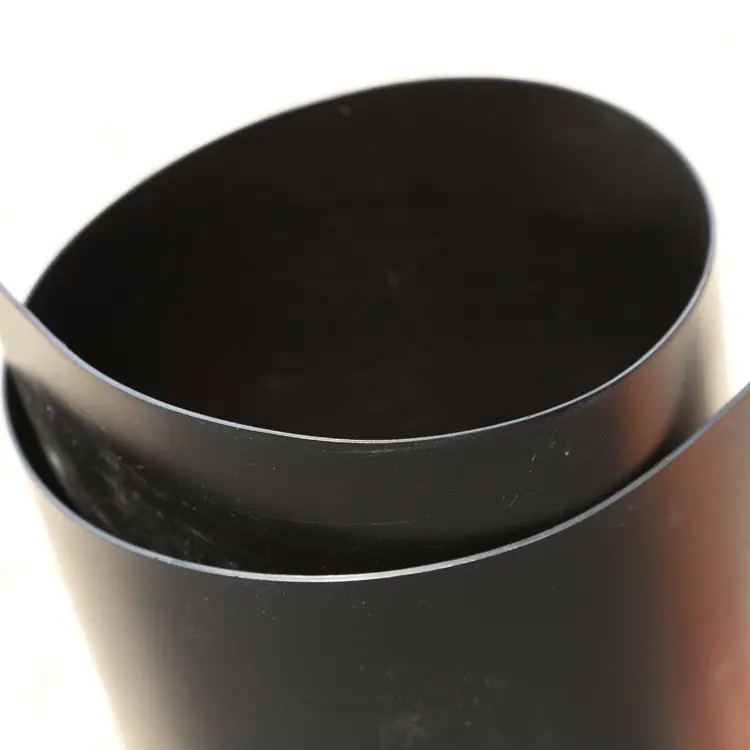

Recycled HDPE Geomembranes: Variations in Appearance and Flexibility
Recycled HDPE Geomembranes, on the other hand, often display a less refined appearance. They may have a matte finish with a rougher texture, a result of the amalgamation of various recycled HDPE sources. These sources may include consumer plastics and industrial waste, each bringing its own set of physical characteristics to the final product. The differences in the original plastic’s age, exposure to elements, and previous usage all contribute to the heterogeneity in appearance. This results in a less uniform surface, which can sometimes exhibit slight color variations or material inconsistencies.
The flexibility of recycled HDPE Geomembranes can also be somewhat limited compared to their virgin counterparts. While still pliable, they may not offer the same level of ease in conforming to complex shapes or enduring mechanical stress without degradation. This reduced flexibility is due to the breakdown of polymer chains during the initial lifecycle of the plastic and the recycling process. Consequently, while still functional for various applications, recycled HDPE Geomembranes might require more careful handling during installation and may not be as forgiving in highly dynamic environments.
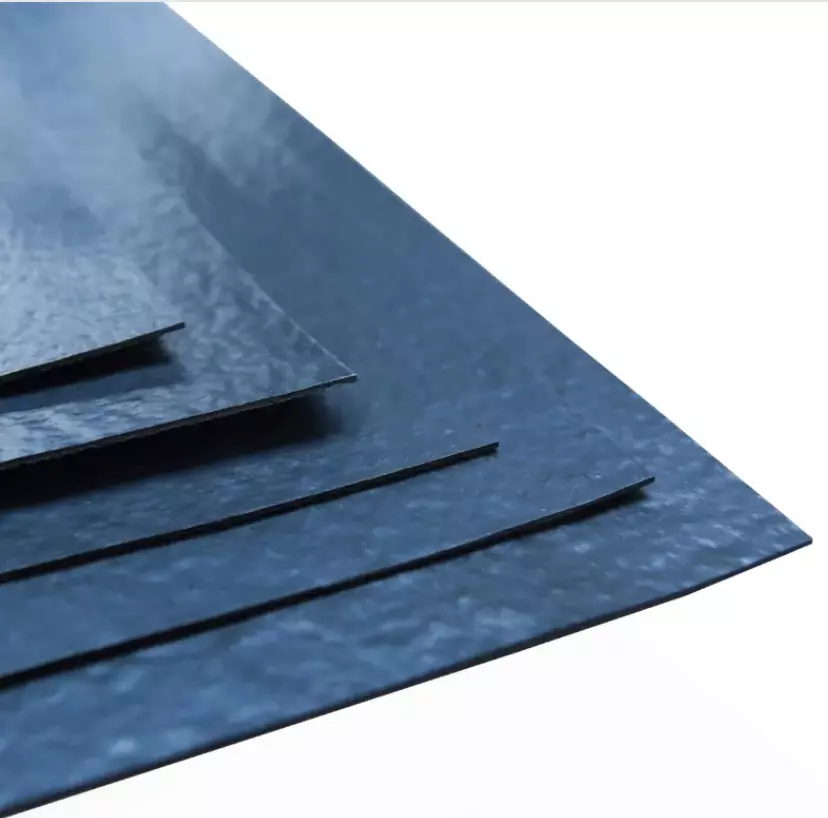
In conclusion, the choice between virgin and recycled HDPE Geomembranes in terms of appearance and flexibility will depend on the specific aesthetic and functional requirements of the project. While virgin materials offer a more polished look and greater adaptability, recycled materials provide a more environmentally sustainable option, albeit with some trade-offs in aesthetic and mechanical properties.
Environmental Impact
Virgin HDPE Geomembranes: Carbon Footprint and Resource Use
Virgin HDPE Geomembranes, despite their high performance and reliability, carry a significant environmental impact primarily due to the processes involved in their production. The manufacturing of virgin HDPE resin granules is resource-intensive, requiring substantial amounts of raw materials and energy. This process involves the extraction and refining of petroleum, a non-renewable resource, which significantly contributes to the carbon footprint of these geomembranes. Additionally, the production process itself releases considerable amounts of greenhouse gases, contributing to global warming and climate change. The environmental cost of virgin HDPE Geomembranes extends beyond their production; their disposal also poses challenges, as they are not biodegradable and can persist in landfills for extended periods, further exacerbating their ecological impact.
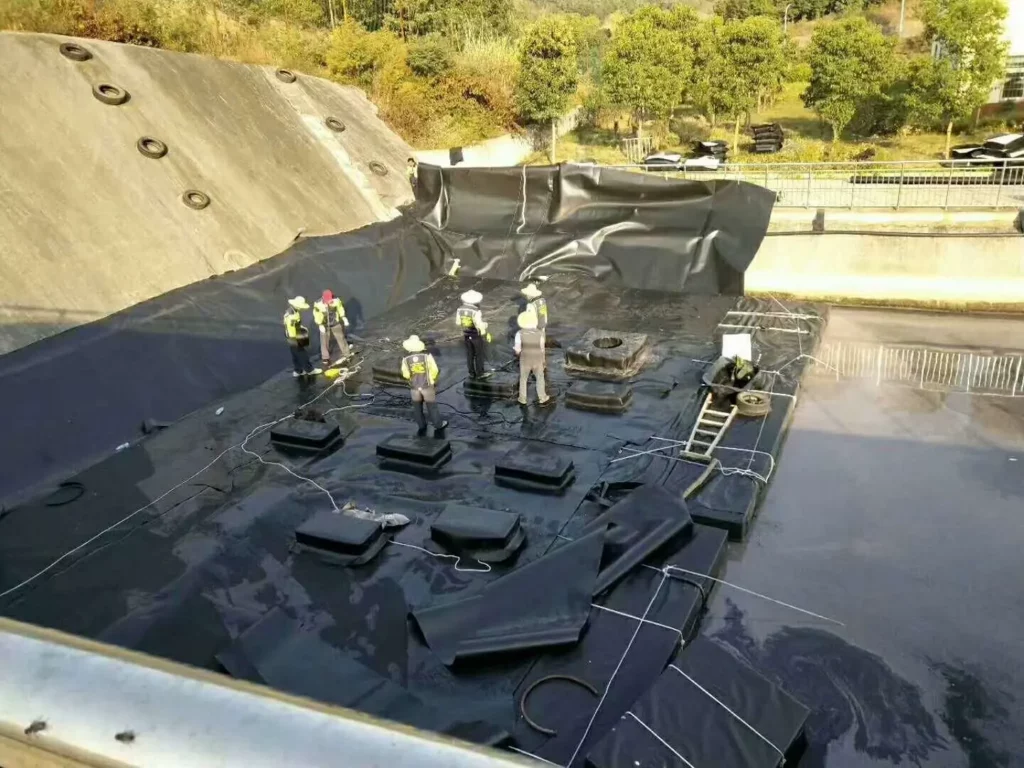

Recycled HDPE Geomembranes: Promoting Sustainability
Recycled HDPE Geomembranes, in contrast, have a much lower environmental impact. By utilizing recycled HDPE resin, these geomembranes help divert plastic waste from landfills and reduce the demand for new plastic production. This recycling process substantially decreases the energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions associated with manufacturing, as recycling HDPE requires significantly less energy compared to producing virgin HDPE. Moreover, the process of recycling HDPE helps mitigate the problem of plastic pollution by giving a second life to materials that would otherwise contribute to environmental degradation.
While recycled HDPE Geomembranes may not match the pristine quality of virgin materials, their environmental benefits are substantial. They play a crucial role in promoting a circular economy, where materials are reused and repurposed, minimizing waste and reducing the strain on natural resources. This makes them an appealing choice for projects and organizations committed to environmental sustainability and reducing their carbon footprint.
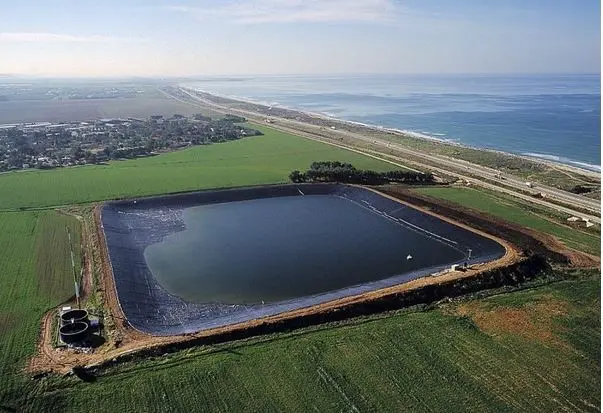

In summary, the environmental impact of HDPE Geomembranes is a critical consideration in their selection. While virgin HDPE offers performance benefits, its environmental cost is higher compared to recycled HDPE, which offers a more sustainable and eco-friendly alternative, aligning with the growing global emphasis on environmental responsibility and sustainable development practices.
Application Suitability
Virgin HDPE Geomembranes: Ideal for High-Stress Applications
Virgin HDPE Geomembranes are the go-to choice for applications where durability and reliability are paramount. Their consistent quality makes them ideal for critical projects such as landfill liners, where they must withstand the corrosive nature of waste and prevent leachate from contaminating the soil and groundwater. Similarly, in hazardous waste containment, the integrity of the geomembrane is crucial to protect the environment from toxic substances.
These geomembranes also excel in applications involving large water bodies, like artificial lakes or irrigation reservoirs, where their high tensile strength and puncture resistance ensure long-term performance without leaks or breaches. In industrial settings, such as in chemical storage or processing plants, the chemical resistance of virgin HDPE Geomembranes makes them a reliable barrier against spills and leaks. Their robustness is also beneficial in mining applications, particularly in tailings dams, where they must endure abrasive materials and fluctuating temperatures.
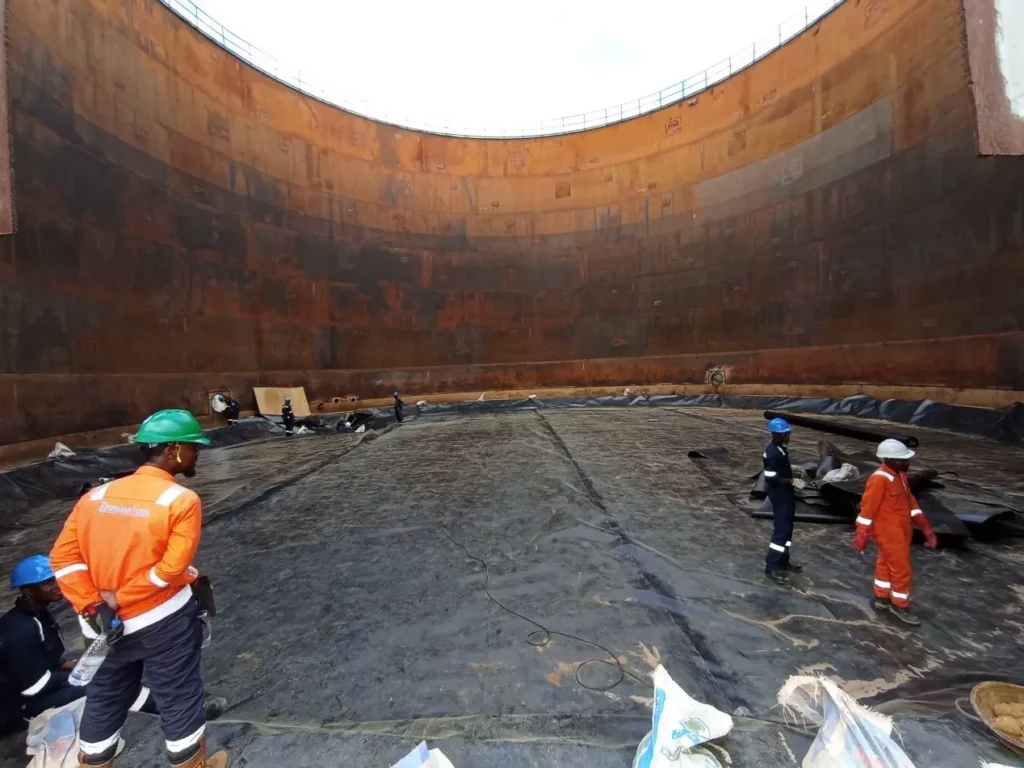

Recycled HDPE Geomembranes: Suited for Less Rigorous Environments
Recycled HDPE Geomembranes, while not as robust as virgin ones, are well-suited for a variety of less demanding applications. They are commonly used in agricultural settings, such as for lining irrigation canals, fish ponds, or water storage reservoirs. In these scenarios, the primary concern is preventing water loss or seepage, and the slightly lower durability of recycled materials is not a significant hindrance.
In environmental conservation projects, like wetland restoration or rainwater harvesting systems, recycled HDPE Geomembranes offer an eco-friendly solution without compromising the project’s effectiveness. They are also suitable for temporary containment solutions, such as in construction sites for managing runoff or in temporary waste storage applications, where their lower cost and reduced environmental impact are advantageous.
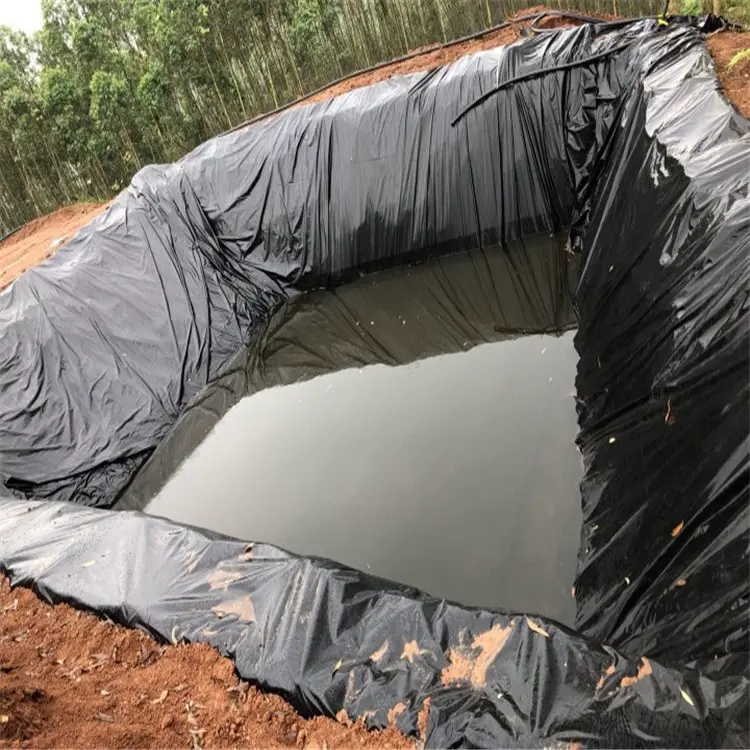

For decorative or recreational water features, like garden ponds or small artificial streams, recycled HDPE Geomembranes provide an economical and environmentally conscious choice. Their adequate performance in these applications, coupled with the benefit of recycling, makes them a practical option for projects with less stringent material requirements.
In conclusion, the selection between virgin and recycled HDPE Geomembranes for specific applications hinges on the balance between performance requirements and environmental considerations. Virgin HDPE is preferred for high-stress, critical applications, where material failure could have severe consequences. In contrast, recycled HDPE is a viable option for projects where the highest level of material performance is not crucial, offering a sustainable choice with lower environmental impact.

Conclusion
In conclusion, the selection between 100% virgin and recycled HDPE Geomembranes for specific applications hinges on the balance between performance requirements and environmental considerations. Virgin HDPE is preferred for high-stress, critical applications, where material failure could have severe consequences. In contrast, recycled HDPE is a viable option for projects where the highest level of material performance is not crucial, offering a sustainable choice with lower environmental impact.




